Welcome to my Mat 301 Calculus I site!
Quiz 3
Sample Questions
Question 1
Find the integral
to the nearest thousandth (3 decimal places).
Answer to Question 1:
See video below for solution.
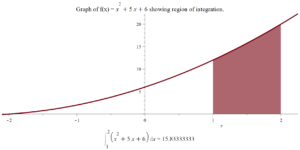
The following Maple commands will calculate the integral (shown above) from Question 1 .
with(plots):
f := x -> x^2 + 5*x + 6:
a := 1:
b := 2:
xStart := -2.1:
xEnd := 2.25:
Int(f(x), x = a .. b) = evalf(int(f(x), x = a .. b));
p1 := plot(f(x), x = xStart .. xEnd, filled = false,
size = [0.7, 0.5], thickness = 6,
title = typeset("Graph of f(x) = ",
f(x), " showing region of integration."),
titlefont = [times, 28],
caption = typeset(Int(f(x), x = a .. b) = evalf(int(f(x),
x = a .. b))), captionfont = [times, 28]):
p2 := plot(f(x), x = a .. b, filled = true, thickness = 6):
display({p1, p2});
Question 2
Find the integral
to the nearest thousandth (3 decimal places).
Answer to Question 2:
See video below for solution.
Question 3
Find the integral
to the nearest thousandth (3 decimal places).
Answer to Question 3:
See video below for solution.
Question 4
Find the integral
to the nearest thousandth (3 decimal places).
Answer to Question 4:
See video below for solution.
Question 5
To the nearest thousandth (3 decimal places), approximate the integral
using a left Riemann sum with a uniform partition of size N = 4.
Answer to Question 5:
See video below for solution.
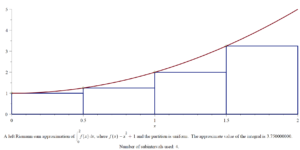
The following Maple commands will calculate the left Riemann sum (shown above) from Question 5 .
with(Student[Calculus1]): f := x -> x^2 + 1; Int(f(x), x = 0 .. 2) = evalf(int(f(x), x = 0 .. 2)); RiemannSum(f(x), x = 0 .. 2, method = left, output = plot, partition = 4, size = [0.7, 0.5], thickness = 4);
Question 6
To the nearest thousandth (3 decimal places), find the integral
Answer to Question 6:
See video below for solution.
Question 7
Find the following limit to the nearest thousandth (3 decimal places)
Answer to Question 7:
See video below for solution.
Notes about limits and L’Hopital’s rule.
We can only use L’Hopital’s rule when the limit is indeterminate, e.g., 0/0.
Example 1.
which is indeterminate of type 0/0, so we could use L’Hopital’s rule to find the limit:
Example 2.
So, the limit is 8. We’re done.
In Example 2 we can’t use L’Hopital’s rule because the limit was not indeterminate.
Of course, if the limit isn’t indeterminate, then we know what the limit is (by substitution, like in Example 2) so there is no need to use L’Hopital’s rule.
The following Maple commands will calculate the limit from Question 7.
f := x -> (cos(2*x)- 1)/(x^2-x); x0 := 0; Limit(f(x), x = x0) = limit(f(x), x = x0);
Question 8
To the nearest thousandth (3 decimal places), find the integral
Answer to Question 8:
See video below for solution.


